
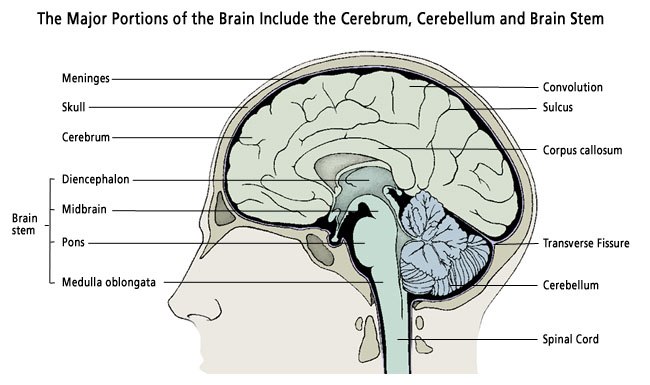
The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.PIXOLOGICSTUDIO/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty ImagesThe brain is made up of billions of neurons and that it also has a number of specialized parts that are each involved in important functions. The brain and the CSF are protected by the The brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem (Fig. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a fluid that provides nourishment and immune protection to the brain, flows around the brain and within the ventricular system (spaces between the regions of the brain). Blood vessels supply oxygen and nutrients to the neurons of the brain. The brain is primarily composed of nerve cells, which are also called neurons.
At the back of the frontal lobe, near the central sulcus, lies the motor cortex.The motor cortex receives information from various lobes of the brain and uses this information to carry out body movements. Frontal LobeThis lobe is located at the front of the brain and is associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher level cognition, and expressive language. The frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe have been associated with different functions ranging from reasoning to auditory perception. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form.The cerebral cortex can be divided into four sections, which are known as lobes.
Damage to the temporal lobe can lead to problems with memory, speech perception, and language skills.The occipital lobe is located at the back portion of the brain and is associated with interpreting visual stimuli and information. This lobe is also the location of the primary auditory cortex, which is important for interpreting sounds and the language we hear.The hippocampus is also located in the temporal lobe, which is why this portion of the brain is also heavily associated with the formation of memories. A portion of the brain known as the somatosensory cortex is located in this lobe and is essential to the processing of the body's senses.The temporal lobe is located on the bottom section of the brain.
It is also associated with motor movement and control, but this is not because the motor commands originate here. It is involved in the coordination of movements as well as motor learning. It receives information from the balance system of the inner ear, sensory nerves, and the auditory and visual systems. The cerebellum is comprised of small lobes and serves a number of important functions.
This gives the hypothalamus a great deal of control over many body functions.The amygdala is a cluster of nuclei located close to the base of the brain. The hypothalamus connects with many other regions of the brain and is responsible for controlling hunger, thirst, emotions, body temperature regulation, and circadian rhythms.The hypothalamus also controls the pituitary gland by secreting hormones. In addition to playing an essential role in motor control, the cerebellum is also important in certain cognitive functions, including speech.Although there is no totally agreed-upon list of the structures that make up the limbic system, four of the main regions include:The hypothalamus is a grouping of nuclei that lie along the base of the brain near the pituitary gland. This allows different muscle groups in the body to act together and produce coordinated fluid movement. The cerebellum helps control posture, balance, and the coordination of voluntary movements.
It is important in memory and learning and is sometimes considered to be part of the limbic system because it plays an important part in the control of emotional responses. The cerebral cortex also sends information to the thalamus, which then sends this information to other systems.The hippocampus is a structure located in the temporal lobe. It is essentially a relay station, taking in sensory information and then passing it on to the cerebral cortex. The structure processes external stimuli and then relays that information to the hippocampus, which can then prompt a response to deal with outside threats.Located above the brainstem, the thalamus processes and transmits movement and sensory information.
Updated May 4, 2021.Hurley RA, Flashman LA, Chow TW, Taber KH. Physiology, cerebral cortex functions. Doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3218-16.2017Jawabri KH, Sharma S. Are the neural correlates of consciousness in the front or in the back of the cerebral cortex? Clinical and neuroimaging evidence.

Updated February 13, 2020.Di Liegro CM, Schiera G, Proia P, Di Liegro I. Brain basics: know your brain. Doi:10.3389/fnhum.2019.00242National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Emotion regulation of hippocampus using real-time fmri neurofeedback in healthy human.
A protocol for a meta-analytic review of randomised controlled trials. Does improving sleep lead to better mental health?. Doi:10.3390/genes10090720Scott AJ, Webb TL, Rowse G.
Association of social contact with dementia and cognition: 28-year follow-up of the Whitehall II cohort study.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
